Project Overview
The goal of this project is to design a modern data pipeline using:
- Loading raw Airbnb datasets into Snowflake from AWS S3 bucket using Storage Integration
- Cleaning, transforming and testing the data with dbt (data-build-tool)
- Modeling key business metrics for occupancy, revenue or income and reviews
- Visualizing insights in Metabase through interactive dashboards
Data Source
Public data from Inside Airbnb – South Aegean, stored in an S3 bucket. Datasets used:
- listings.csv.gz – Metadata for each listing
- calendar.csv.gz – Daily availability and pricing
- reviews.csv.gz – Guest reviews and review dates
To identify the data structure, missing values, outliers, and potential data quality issues such as inconsistent formats or invalid entries, I used the DataPrep data profiling tool for an initial data assessment and quality check.
Data Pipeline
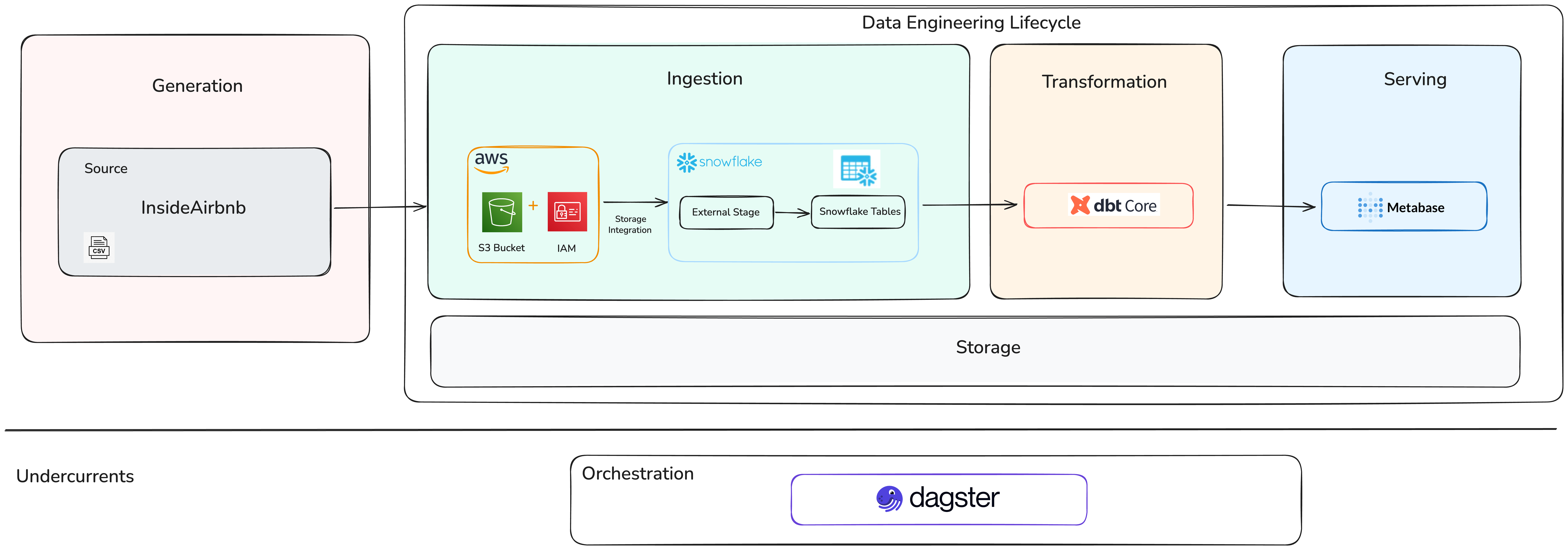
The data pipeline uses a modern and modular stack. The process starts with [InsideAirbnb](https://insideairbnb.com/get-the-data/) , which provides open Airbnb data.
- Snowflake: Cloud data warehouse for storage
- dbt: Data modeling (dimensional), transformation, testing, and documentation
- SQL: Core transformation language
- Metabase: Dashboard and data visualization
Key Metrics Modelled
🏠 Market Overview
- Total Listings by location, room type, rental type
- Average nightly price by location (neighbourhood, island)
(dim_listing × dim_location)
💰 Occupancy & Income
- Average income by location, by season per host, by room or property type Income Trend
- Average income per host
- by location
- by season
- by property type
→ Insight: Identify which areas or property types are growing or declining in profitability
- Top income-generating neighbourhoods and islands
📊 Occupancy Trends
- Occupancy rate over time (daily / weekly / monthly)
- Seasonal occupancy per location or property type (season)
- Average occupancy rates over time by location and time
⭐ Reviews
- Review volume over time
- Review sentiment
Pipeline
1) Ingestion (Snowflake + S3)
- Storage Integration: S3 role trust + stage (
S3_AIRBNB_STAGE) - Load Strategy:
- Method 1: Explicit schema (strict contracts)
- Method 2:
INFER_SCHEMA(rapid prototyping)
- Landing Zone:
RAWschema tables forlistings,calendar,reviews
2) Transformation (dbt)
Layer overview
Project follows a dbt layered approach:
- Staging (
stg_*): Direct, minimally transformed 1:1 reflections of raw sources, column standardization & light cleaning.-
stg_calendar
- Grain: listing_id × calendar_date (one row per listing per date appearing in source).
- Purpose: Pass through availability & nightly constraints.
- Normalization: Denormalized relative to source; acceptable at staging.
-
stg_listings- Grain: listing_id (one row per listing snapshot in the source; filtered where price not null).
- Contains host, neighbourhood, pricing, review score attributes. Quite wide and intentionally not normalized here.
- Normalization: Low (host + location + listing details together). Appropriate for staging.
stg_reviews- Grain: review_id (unique review per listing).
- Normalization: Minimal; raw review text carried forward.
- Dimensions (
dim_*): Conformed, surrogate-keyed entities.-
dim_date
- Grain: date_day (unique calendar date).
- Key:
date_key(YYYYMMDD numeric surrogate). - Normalization: Fully atomic (1 row per date). Pure time dimension.
-
dim_host- Grain: host_id (distinct hosts from listings).
- Key:
host_keysurrogate; natural key host_id retained. - Normalization: Moderate with derived attributes (segment, tenure) live here instead of separate tables (fine for analytics star schema).
dim_location- Grain: (neighbourhood_raw, island_name) pair; surrogate
neighbourhood_key. - Attributes: island_group for hierarchical rollups.
- Normalization: Slight snowflaking could split island vs neighbourhood, but current design keeps hierarchy in one table—pragmatic.
- Grain: (neighbourhood_raw, island_name) pair; surrogate
dim_listings- Grain: listing_id.
- Key:
listing_keysurrogate. - Foreign keys:
host_key,neighbourhood_key. - Contains classification buckets (size, bedroom_category, price_category, review_category, availability_category) and derived metrics (estimated_occupancy_rate_pct).
- Normalization: Intentional denormalization for performance/readability; star schema center dimension.
dim_calendar- Grain: listing_key × date_key.
- Key:
calendar_keysurrogate (bridge). - Acts like a periodic snapshot dimension / bridge between date & listing with availability attributes.
- Normalization: Proper (each atomic combination once). Serves as base for occupancy fact.
- Facts (
fct_*/ incremental). Events taken:-
fct_occupancy
- Grain: listing_key × date_key (daily).
- Measures: is_available (degenerate boolean), nightly_price (copied from listing), plus dimension foreign keys (neighbourhood_key, host_key).
- Type: Transactional-ish / periodic snapshot fact.
- Normalization: Standard fact table referencing conformed dims.
-
fct_reviews- Grain: review_id (each review event).
- Measures/Attributes: sentiment_compound, sentiment_label.
- Foreign linkage: listing_key (fact-to-dim join).
- Normalization: Proper atomic event fact.
- Enhancements: Calculated sentiment score and category with UDF using Vader from python. 160,290 out of 976,657 is approximately 16.41% rows have sentiment_compound 0, indicating reviews written other than english.
- Used LanguageDetector to identify the language but will omit the translating due to costs (API or Snowflake Cortex AI)
- Marts (
mart_*): Aggregated, analytics-ready rollups.
3) Visualization (Metabase)
Running Metabase with docker. There are other options to run the Metabase server, as a Java JAR file, Metabase Cloud (free trial exists).
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name metabase metabase/metabaseOpen http://localhost:3000
Dashboards
Market Overview
- Total listings by island, neighbourhood, and room type
- Average price by location
- Distribution of property types ![[Pasted image 20251114000745.png]]
Occupancy & Income
- Occupancy trends (daily/weekly/monthly)
- Income per host by location, season, and property type
- Top-performing neighbourhoods ![[Pasted image 20251114000803.png]] Reviews & Sentiment
- Review volume over time
- Positive/neutral/negative sentiment
- Location-level sentiment differences ![[Pasted image 20251114000721.png]]
4) Orchestration
requirements
uv add dagster-dbt
uv add dagster-webserverinitiate dagster
dagster-dbt project scaffold --project-name dbt_dagster_project_airbnb --dbt-project-dir=airbnbrun dagster server
uv dagster devChallenges
- Availability ≠ booking certainty: treat “unavailable” as proxy; clearly flag in metrics and dashboards. - Is_available doesn't necessarily mean the listings is booked, it could be disabled by the host, by private booking etc. From publicly available (scraped data) we cannot know this information surely. That's why the fact table is called fact_occupancy but the general assumption to calculate price related metrics, non available dates will be considered as booked.
- This data model doesn’t have time-varying prices.
Key Takeaways
- Gained practical experience using Snowflake, modelling with dbt using a layered architecture.
- Learned a new tool to build interactive dashboards in Metabase and structure them around key business questions (occupancy, revenue, reviews).
Further Enhancements
- Automate ingestion when new data is loaded into S3 bucket
- SCD type 2 for listings
